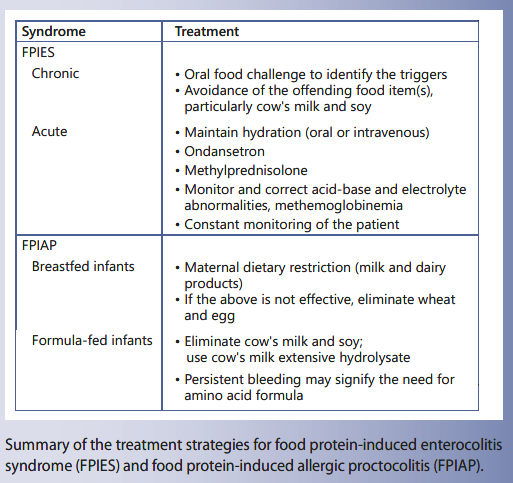
food protein induced enterocolitis syndrome fpies adults
Medical records of children with DS diagnosed at our hospital between 2000 and 2019 were retrospectively reviewed. Individuals with FPIES experience profuse vomiting and diarrhea that usually develops.

Food Protein Induced Enterocolitis Syndrome Oral Food Challenge Annals Of Allergy Asthma Immunology
Learn more about FPIES and how Neocate can help.
. Food Protein-Induced Enterocolitis Syndrome FPIES is a type of food allergy affecting the gastrointestinal GI tract. Food protein-induced enterocolitis FPIES is a food allergy that mostly affects infants and young children. About Food Protein-Induced Enterocolitis Syndrome.
FPIES is caused by an immune reaction triggered by common foods and is not an IgE-mediated food allergy. FPIES typically occurs in the first year of life. J Allergy Clin Immunol.
Food Protein-Induced Enterocolitis Syndrome FPIES sometimes referred to as a delayed food allergy is a severe condition causing vomiting and diarrhea. 1 In 1967 one of the first case descriptions of FPIES by Gryboski described 21 hospitalized patients diagnosed with gastrointestinal milk allergy that presented with symptoms of chronic. In some cases symptoms can progress to dehydration and shock brought on by low blood pressure and poor blood circulation.
Food Protein-Induced Enterocolitis Syndrome FPIES is a systemic non IgE-mediated response to a specific trigger within food - most likely food proteinFPIES presents in two different forms. Symptoms such as paleness and lethargy fatigue also may occur. Food-protein induced enterocolitis syndrome FPIES is a non-IgE-mediated reaction affecting predominantly infants and children.
Food protein-induced enterocolitis syndrome FPIES is a non-immunoglobulin E IgE mediated gastrointestinal food hypersensitivity that manifests as profuse repetitive vomiting sometimes with diarrhea leading to dehydration and lethargy in the acute setting or chronic watery diarrhea with intermittent vomiting leading to weight loss failure to. Symptoms are primarily gastrointestinal including repetitive vomiting and sometimes diarrhea. Symptoms of vomiting and bloody diarrhea can lead to dehydration andor shock after consumption of certain foods.
Unlike most food allergies symptoms of FPIES do not begin immediately after eating. Acute FPIES reactions typically present with delayed repetitive vomiting lethargy and pallor within 1 to 4 hours of food ingestion. A majority of cases occur during infancy particularly with the early introduction of additional foods.
Mane SK Bahna SL. Fernandes BN Boyle RJ Gore C Simpson A Custovic A. An acute form and a chronic form.
Like other food allergies FPIES reactions are triggered by eating a particular food. FPIES is an allergic reaction to food in the digestive tract. FPIES symptoms can be very serious and can include turning grey or blue dehydration and even going into shock.
Classic symptoms of FPIES include profound vomiting diarrhea and dehydration. It typically causes vomiting and bloody diarrhea after consumption of certain foods the trigger foods arent the same for everyone. Food protein-induced enterocolitis syndrome FPIES is a non-immunoglobin E-mediated food hypersensitivity disorder.
Symptoms include severe vomiting and diarrhea and usually occur 2-3 hours after eating a food. Food Protein Induced Enterocolitis Syndrome FPIES is a type of non-IgE mediated food allergy that can present with severe vomiting diarrhea and dehydration. In its acute form FPIES presents with vomiting that usually begins 1 to 4 hours after trigger food ingestion can be 30 minutes to 6 or more hours.
Food protein-induced enterocolitis syndrome FPIES is an uncommon disorder characterized by an allergic reaction to food that affects the gastrointestinal system. Among the 43 children with DS five 116. In this study we report a Canadian cohort of 19 adolescents and adults with recurrent non-immunoglobulin E IgE-mediated gastrointestinal symptoms after crustacean ingestion consistent with FPIES.
Food protein-induced enterocolitis syndrome FPIES is a condition that occurs in infants and young children although it can rarely affect older children or adults as well. The FPIES Foundation Board of Directors and Medical Advisory Board. The term enterocolitis specially refers to inflammation of the small and large intestines.
Food protein-induced enterocolitis syndrome FPIES is a rare non-immunoglobulin E-mediated gastrointestinal food allergy primarily diagnosed in infancy but has also been reported in older children and adults. Food protein-induced enterocolitis FPIES an entity previously thought to only affect children has been increasingly described in adults. Written in collaboration by.
Food Protein-Induced Enterocolitis Syndrome FPIES is an inflammation involving both the small intestine and the large intestine colon. FOOD PROTEIN INDUCED ENTEROCOLITIS SYNDROME FPIES FPIES typically affects children under the age of one year. Food protein-induced enterocolitis syndrome is also called FPIES pronounced like the letter f followed by the word pies If youve never heard of it allow us to help.
However little is known about the clinical features of FPIES in patients with Down syndrome DS. Instead it can take hours before severe symptoms begin. Food Protein-Induced Enterocolitis FPIES Food protein-induced enterocolitis syndrome FPIES is a non-IgE-mediated gastrointestinal food hypersensitivity that affects the entire gastrointestinal tract.
Food protein-induced enterocolitis FPIES an entity previously thought to only affect children has been increasingly described in adults. Curr Opin Allergy Clin Immunol. The most common triggers include cow milk soy and grains rice barley oats.
The International FPIES Food Protein-Induced Enterocolitis Syndrome Association is a recognized 501c3 nonprofit corporation and organization that provides education support and advocacy for individuals with Food Protein-Induced Enterocolitis Syndrome FPIES and. In this study we report a Canadian cohort of 19 adolescents and adults with recurrent non-immunoglobulin E IgE-mediated gastrointestinal symptoms after crustacean ingestion consistent with FPIES. Adult cases have been recently reported but are rare.
Food protein-induced enterocolitis syndrome FPIES is a rare food allergy that affects the gastrointestinal GI tract. Food protein-induced enterocolitis syndrome can occur in adults. Clinical manifestations of food protein-induced enterocolitis syndrome.

Food Protein Induced Enterocolitis Syndrome Annals Of Allergy Asthma Immunology

Dietary Management Of Food Protein Induced Enterocolitis Syndrome During The Coronavirus Disease 2019 Pandemic Annals Of Allergy Asthma Immunology

Managing Food Protein Induced Enterocolitis Syndrome During The Coronavirus Disease 2019 Pandemic Annals Of Allergy Asthma Immunology
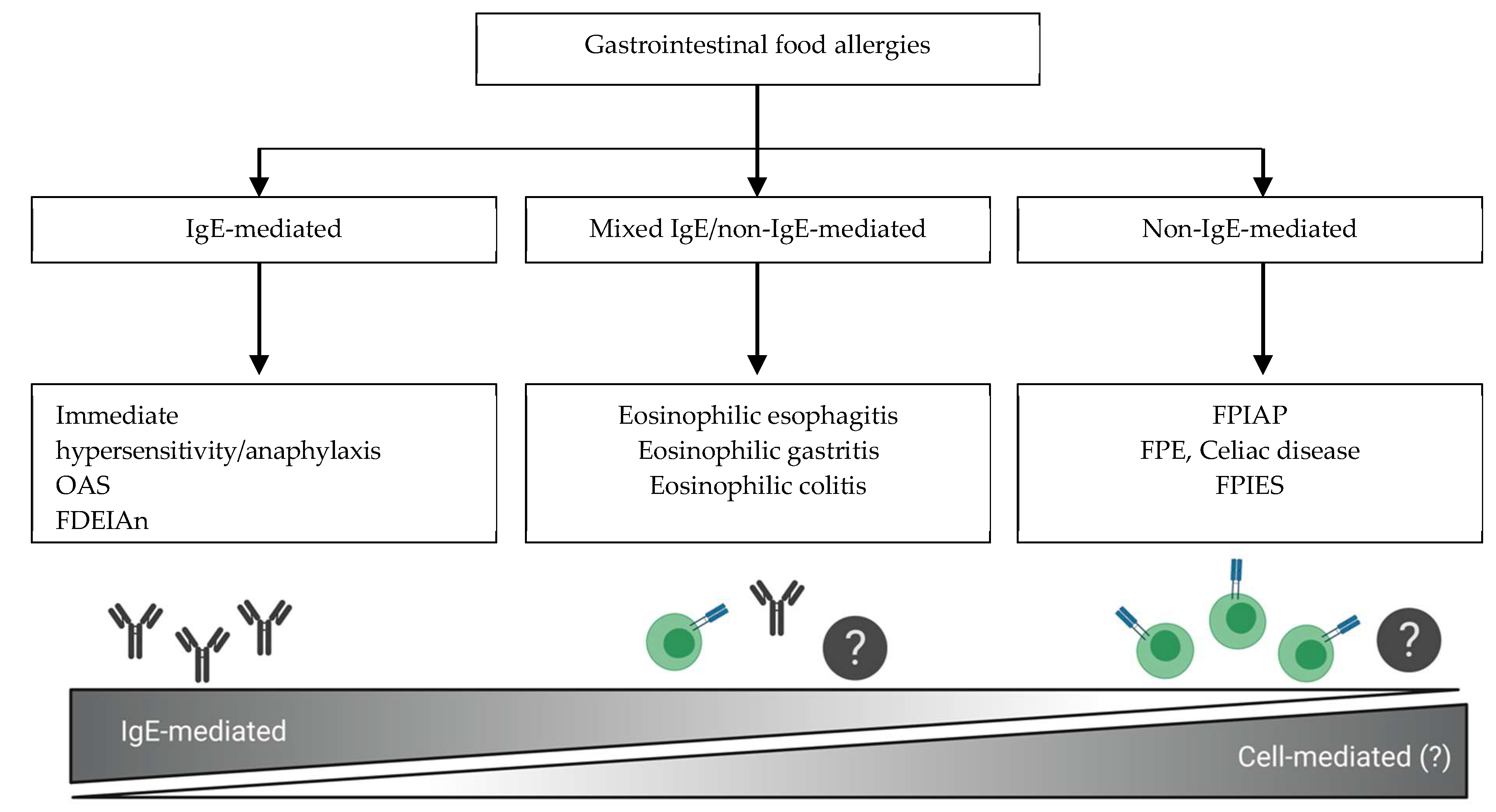
Nutrients Free Full Text Non Ige Mediated Gastrointestinal Food Allergies In Children An Update Html

References In Food Protein Induced Enterocolitis Syndrome The Journal Of Allergy And Clinical Immunology In Practice

References In Food Protein Induced Enterocolitis Syndrome Not So Rare After All Journal Of Allergy And Clinical Immunology

Food Protein Induced Enterocolitis Syndrome And Proctocolitis
Two Case Reports Of Food Protein Induced Enterocolitis

References In Immunopathophysiology Of Food Protein Induced Enterocolitis Syndrome Journal Of Allergy And Clinical Immunology